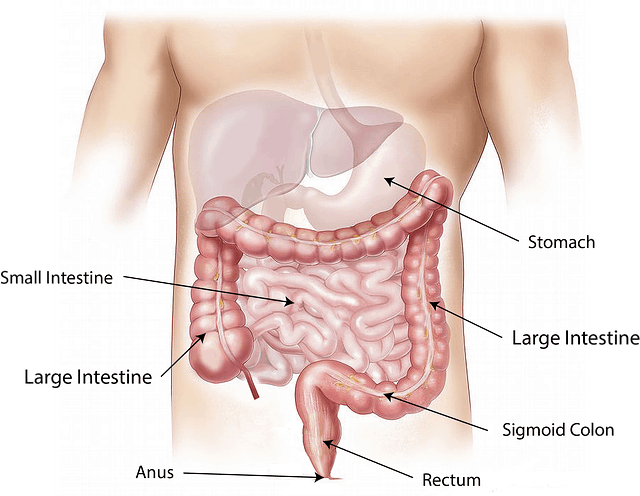
APPENDICITIS is an inflammation of the appendix, a finger-shaped pouch that projects from your colon on the lower right side of your abdomen.
The appendix does not seem to have a specific purpose. A blockage in the lining of the appendix that results in infection is the likely cause of appendicitis. The bacteria multiply rapidly, causing the appendix to become inflamed, swollen and filled with pus. If not treated promptly, the appendix can rupture. Signs and symptoms of appendicitis may include; sudden pain that begins on the right side of the lower abdomen and sudden pain that begins around your navel and often shifts to your lower right abdomen. Symptoms may also include pain that worsen if you cough, walk or make other jarring movements. Nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite and abdominal bloating have also been reported. Other signs such as diarrhea, constipation or low-grade fever that worsen as the illness progresses may also occur.
Appendicitis can cause serious complications such as a ruptured appendix which spreads infection throughout your abdomen (peritonitis). Possibly a life threatening illness, this condition requires immediate surgery to remove the appendix and clean your abdominal cavity.
Appendiceal Abscess is a pocket of infection with fluid and pus collection. An abscess requires drainage and the surgeon often place a tube in the abdomen through the abdominal wall for a few days to help drain and clear the infection while administering antibiotics.
To help diagnose appendicitis, your doctor will likely take a history of your signs and symptoms and examine your abdomen. Blood test can also be done to establish whether the white cell count is high. Urine test can also help to exclude urinary tract infection or kidney stones. Abdominal ultrasound or computerised tomography (CT) scan can also be carried out to confirm appendicitis.
In the female population and due to gynaecological problems that often time mimics appendicitis, the doctor will perform a comprehensive pelvic examination to exclude gynaecological pathology such as ovarian cyst, pelvic inflammatory disease and fibroid uterus. When in doubt, the doctor will always request pelvic sonar to ascertain the diagnosis.
Make an appointment with a doctor if you have worrisome signs or symptoms. Severe abdominal pain requires immediate medical attention. Appendicitis treatment usually involves surgery to remove the inflamed appendix. Before surgery, you may be given a dose of antibiotics to prevent further inflammation and spread of infection.
Dr. Makemba Shayela Nelson – MBChB – University of Kwazulu-Natal, Durban, South Africa. Nesha Medical Practice.